Heal Your Gut, Transform Your Life: The Mind-Gut Connection Explained
Heal Your Gut, Transform Your Life: The Mind-Gut Connection Explained
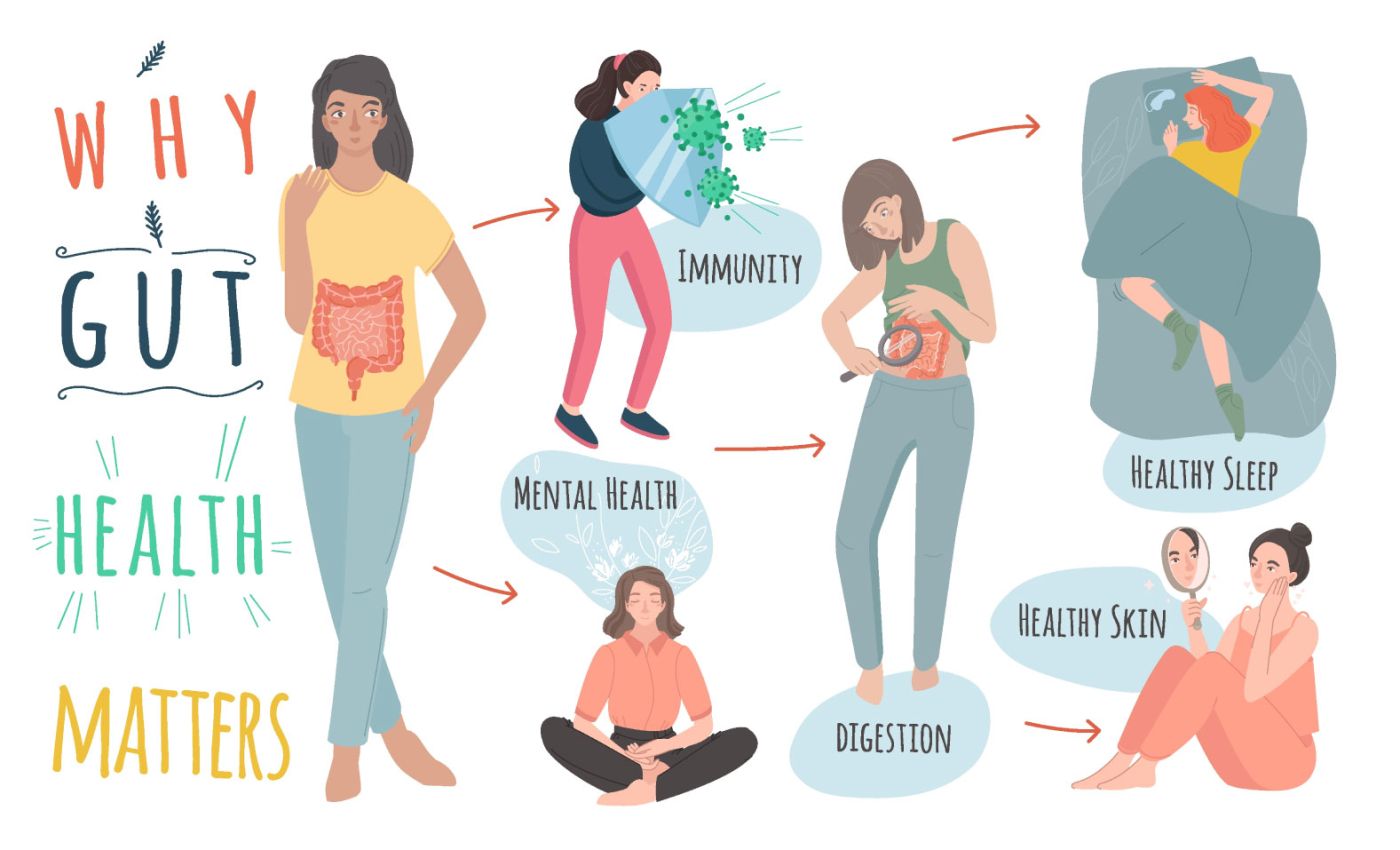
In recent years, science has made fascinating discoveries about the gut’s role in overall well-being, especially in relation to mental health. It turns out that the gut and brain are intricately connected through a bi-directional communication system known as the gut-brain axis. This relationship goes deeper than you might think: a healthy gut can positively influence your mood, cognition, and even immune system, while an unhealthy gut can lead to numerous physical and psychological issues. This blog delves into the importance of gut health, explains the mind-gut connection, and provides actionable steps to help you nurture this crucial relationship for a healthier, happier life.
The Importance of Gut Health
Our digestive system is home to trillions of microbes, primarily bacteria, which make up the gut microbiome. These microbes perform essential functions such as aiding digestion, synthesizing vitamins, and protecting against pathogens. The balance of good and bad bacteria in our gut can impact everything from physical health to mood and mental clarity. When this balance is disrupted, issues like inflammation, digestive disorders, anxiety, and even depression can arise.
Understanding the Mind-Gut Connection
The gut is often called the “second brain” because it contains millions of neurons and is capable of producing neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which are essential for mood regulation, cognition, and sleep. The gut and brain communicate through a network of neurons, hormones, and chemicals, collectively known as the gut-brain axis. This connection allows them to send signals back and forth, influencing each other’s functions.
Key Pathways in the Mind-Gut Connection
- Vagus Nerve: This nerve runs directly from the brain to the gut, acting as a primary pathway for communication. Signals sent through the vagus nerve influence digestion, metabolism, and stress response.
- Immune System: The gut plays a significant role in immunity. When the gut’s microbiome is imbalanced, it can lead to inflammation, which is linked to mood disorders and immune issues.
- Neurotransmitters: The gut produces about 90% of the body’s serotonin, a key hormone that stabilizes mood. An imbalance in gut bacteria can affect serotonin levels and, in turn, influence mental well-being.
Signs Your Gut Might Be Out of Balance
Gut imbalance, or dysbiosis, can manifest in various ways. Here are some common signs that your gut may need attention:
- Digestive Issues: Symptoms like bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea can indicate an imbalance in gut bacteria.
- Food Intolerances: When your gut is unbalanced, it may react poorly to certain foods, causing sensitivities or allergies.
- Frequent Illnesses: Since the gut is central to immune health, a compromised gut can make you more susceptible to infections.
- Mood Swings and Anxiety: The gut-brain connection means that an unhealthy gut can contribute to mood swings, anxiety, and even depression.
- Fatigue and Poor Sleep: Gut health impacts melatonin production and sleep quality, so a disturbed microbiome can lead to insomnia and low energy levels.
How to Heal Your Gut and Boost the Mind-Gut Connection
Improving gut health is key to strengthening the mind-gut connection. Here are practical ways to support your gut and, in turn, boost mental and physical well-being:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet Rich in Fiber and Whole Foods
- Focus on Prebiotics and Probiotics: Prebiotics (such as garlic, onions, and bananas) feed the good bacteria in your gut, while probiotics (such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods) introduce beneficial bacteria to the microbiome.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugar: Highly processed foods and refined sugars can increase harmful bacteria and promote inflammation, which disrupts gut health.
2. Incorporate Fermented Foods
- Fermented foods like curd (dahi), idli, dosa, and pickles are rich in probiotics. They naturally replenish good bacteria, helping to restore gut balance and improve digestion.
- Kombucha, kimchi, and sauerkraut are other good options if you want to expand your choices.
3. Stay Hydrated
- Drinking enough water supports healthy digestion and keeps the mucosal lining of the gut well-lubricated. Hydration is essential for maintaining a balanced gut environment.
4. Manage Stress Levels
- Chronic stress can alter the composition of gut bacteria, leading to gut issues and affecting mental well-being. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote a healthy gut-brain connection.
5. Get Regular Exercise
- Physical activity is beneficial not only for the body but also for the gut. Exercise promotes healthy digestion, encourages the growth of beneficial bacteria, and supports the production of gut-friendly short-chain fatty acids.
6. Ensure Good Sleep Quality
- Quality sleep is crucial for gut health. Disrupted sleep patterns can negatively impact the microbiome, so aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night. Establishing a sleep routine and avoiding screens before bed can help improve sleep quality.
7. Avoid Unnecessary Antibiotics
- Antibiotics can kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria in the gut. Use them only when necessary, and always follow up with probiotics to restore healthy bacteria levels after a course of antibiotics.
Foods to Include for a Healthy Gut in India
Here’s a list of some commonly available foods in India that support a healthy gut and strengthen the mind-gut connection:
- Curd (Dahi) – A staple in Indian diets, curd is rich in probiotics and aids in digestion.
- Buttermilk (Chaas) – Cooling and probiotic-rich, buttermilk is ideal for maintaining gut health.
- Idli and Dosa – Fermented rice and urad dal dishes that are easy to digest and support good bacteria growth.
- Whole Grains (Jowar, Bajra, Ragi) – High in fiber, these grains act as prebiotics, feeding the beneficial bacteria.
- Garlic and Onions – Widely used in Indian cuisine, these are excellent prebiotics that help foster a healthy gut environment.
- Bananas (Kela) – Rich in fiber and easy to digest, bananas are a great prebiotic food.
The Benefits of a Healthy Gut and Strong Mind-Gut Connection
- Enhanced Mood and Reduced Anxiety: A balanced gut can improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Better Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: Improved digestion leads to better absorption of essential nutrients, promoting overall health.
- Stronger Immunity: A healthy gut bolsters the immune system, reducing the frequency of infections and illnesses.
- Improved Mental Clarity and Focus: With a balanced microbiome, mental clarity and cognitive functions can improve, supporting better focus and productivity.
- Increased Energy Levels: Better digestion and nutrient absorption translate into higher energy levels and reduced fatigue.
Conclusion
The mind-gut connection highlights how closely our mental and physical health are intertwined with gut health. By nurturing our gut through balanced nutrition, stress management, and healthy lifestyle habits, we can unlock a cascade of positive effects that extend to both body and mind. Small daily choices in diet and lifestyle can lead to profound improvements in gut health, mental clarity, and emotional resilience.
So, start with simple steps like adding fermented foods to your diet, staying active, managing stress, and paying attention to the quality of your sleep. Over time, these changes will help you heal your gut and, in doing so, transform your life for the better.
Buy Now | Available for delivery across India.
Order Holistic products now and experience the benefits of Ayurveda.
Explore Holistic Health Products